How to Prepare for and Survive a Natural Disaster?
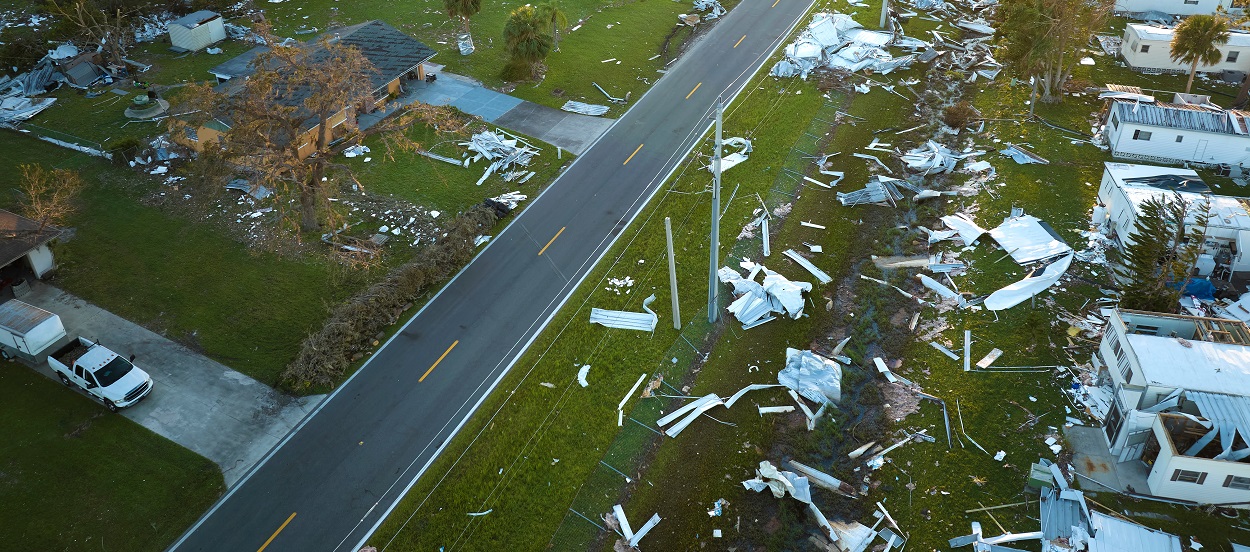

Natural disasters can strike without warning, leaving devastation in their wake. Whether you live in an earthquake-prone region, a coastal area susceptible to hurricanes, or a place where wildfires are a concern, being prepared for these events is essential for your safety and the well-being of your loved ones. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore how to prepare for and survive a wide range of natural disasters, each with its unique challenges and considerations. From earthquakes and floods to wildfires and tornadoes, understanding the steps you can take to safeguard yourself and your community is crucial. Let's dive into the strategies and precautions that can make all the difference when facing the forces of nature.
But first, here is a list of some common natural disasters:
-
Earthquakes: Sudden shaking or movement of the Earth's crust, often resulting in structural damage and tsunamis.
-
Volcanic Eruptions: The eruption of molten rock, ash, and gases from volcanoes, can cause destruction and ashfall.
-
Tornadoes: Violently rotating columns of air that extend from thunderstorms to the ground, causing devastating wind damage.
-
Hurricanes (Typhoons or Cyclones): Powerful tropical storms with high winds and heavy rainfall, leading to flooding and storm surges.
-
Floods: Overflow of water onto normally dry land, often caused by heavy rainfall, storm surges, or dam failures.
-
Tsunamis: Large ocean waves generated by underwater earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, or landslides.
-
Wildfires: Uncontrolled fires that spread rapidly through vegetation, often exacerbated by dry conditions and strong winds.
-
Droughts: Prolonged periods of abnormally low rainfall, leading to water shortages and crop failures.
-
Landslides: The sudden downhill movement of rock, soil, and debris, often triggered by heavy rainfall or earthquakes.
-
Tropical Storms: Lesser intense storms than hurricanes, but still capable of causing significant damage through heavy rainfall and winds.
-
Blizzards: Severe snowstorms with low visibility and strong winds, leading to snow accumulation and transportation disruptions.
-
Heatwaves: Extended periods of excessively high temperatures, which can have adverse effects on human health and ecosystems.
-
Avalanches: Rapid movement of snow, ice, and debris down a mountain slope, often triggered by factors like snowfall or human activity.
-
Hailstorms: Severe thunderstorms that produce large, damaging hailstones.
-
Mudslides: Rapid flow of mud, water, and debris down slopes, often following heavy rainfall.
-
Sinkholes: Sudden collapses in the ground surface, often caused by the dissolution of underground limestone or other geological processes.
-
Tidal Waves: Large and powerful waves caused by gravitational forces, typically associated with the movement of the moon and sun.
-
Tornados: Violent windstorms characterized by a twisting, funnel-shaped cloud, capable of causing severe damage.
-
Winter Storms: Severe weather events in winter, including heavy snow, freezing rain, and ice storms.
-
Haboobs: Dust storms or sandstorms that occur in arid regions, reducing visibility and causing respiratory issues.
It's important to note that these natural disasters can vary in intensity and impact depending on factors such as location, climate, and geographical conditions. Preparedness and mitigation efforts are crucial to minimizing the damage caused by these events.
Below is a brief list of how to prepare for and survive each natural disaster.
Earthquakes
Preparation:
- Secure heavy furniture and appliances to prevent them from toppling over.
- Develop an emergency communication plan with family and neighbors.
- Build an emergency kit with food, water, first aid supplies, and flashlights.
- Identify safe spots within your home and practice "Drop, Cover, and Hold On."
- Retrofit your home to withstand seismic activity if you live in a high-risk area.
Survival:
- Stay indoors, away from windows, glass, and heavy objects.
- Protect your head and neck if you can't find shelter.
- After the shaking stops, check for injuries and provide first aid.
- Be prepared for aftershocks and follow local authorities' instructions.
Volcanic Eruptions
Preparation:
- Stay informed about local volcano activity and evacuation plans.
- Create an emergency kit with masks, goggles, and non-perishable food.
- Develop an evacuation plan with multiple routes.
- Protect your home from ashfall by sealing windows and doors.
Survival:
- Evacuate promptly if authorities issue evacuation orders.
- If caught in an ashfall, cover your nose and mouth with a cloth.
- Stay indoors and avoid driving in heavy ashfall conditions.
- Listen to authorities for updates on volcanic activity.
Tornadoes
Preparation:
- Install a tornado shelter or identify a safe room in your home.
- Develop a family tornado plan with a designated meeting place.
- Create an emergency kit with a battery-operated weather radio.
- Stay informed about local tornado watches and warnings.
Survival:
- Seek shelter in the lowest, most central part of your home.
- Protect yourself from flying debris by covering with a mattress or heavy blankets.
- Listen to weather updates on a battery-operated radio.
- Avoid mobile homes and cars during tornado warnings.
Hurricanes (Typhoons or Cyclones)
Preparation:
- Evacuate if you're in an evacuation zone.
- Secure your home with hurricane shutters or plywood.
- Stock up on non-perishable food, water, and essential supplies.
- Keep important documents in a waterproof container.
- Prepare a family communication plan.
Survival:
- Stay indoors during the storm and away from windows.
- Avoid floodwaters, which may be contaminated or have strong currents.
- After the storm, be cautious of downed power lines and flooding.
Floods
Preparation:
- Know your area's flood risk and evacuation routes.
- Elevate electrical systems and install sump pumps.
- Secure important documents in waterproof containers.
- Create a flood emergency kit with food, water, and first aid supplies.
Survival:
- Evacuate if authorities recommend it; don't attempt to drive through floodwaters.
- Move to higher ground if flooding occurs and stay there until it's safe to return.
- Listen to emergency broadcasts for updates and instructions.
Tsunamis
Preparation:
- Familiarize yourself with tsunami warning signs and evacuation routes.
- Create a family emergency plan with designated meeting places.
- Assemble a disaster kit with food, water, and essential supplies.
- Know the difference between local and distant tsunami warnings.
- Educate yourself about the natural warning signs, such as strong ground shaking or the ocean rapidly receding.
Survival:
- Evacuate immediately if a tsunami warning is issued; do not wait for confirmation.
- Head to higher ground or move inland as quickly as possible.
- If you cannot escape in time, move to a higher floor or rooftop.
- Do not return to coastal areas until authorities declare it safe.
Wildfires
Preparation:
- Create a defensible space around your property by clearing vegetation.
- Install spark arresters on chimneys and secure eaves and vents.
- Develop a family evacuation plan with escape routes.
- Maintain an emergency kit with N95 masks, goggles, and fire-resistant clothing.
- Stay informed about local fire conditions and restrictions.
Survival:
- Evacuate immediately when authorities issue evacuation orders.
- If trapped, seek shelter in a building, car, or clear area devoid of vegetation.
- Cover yourself with non-flammable materials like wool blankets.
- Stay low to the ground to avoid smoke inhalation.
Droughts
Preparation:
- Conserve water by fixing leaks and using water-efficient appliances.
- Plant drought-resistant vegetation and reduce outdoor water use.
- Stockpile emergency water supplies in case of water shortages.
- Develop a plan for preserving food and managing crops during dry periods.
- Stay informed about drought conditions and local water restrictions.
Survival:
- Practice water conservation techniques to extend your water supply.
- Reduce outdoor water usage and avoid unnecessary water consumption.
- Stay updated on drought forecasts and follow local water conservation guidelines.
Landslides
Preparation:
- Identify landslide-prone areas in your vicinity.
- Develop a family evacuation plan and establish safe meeting places.
- Monitor rainfall and weather conditions during wet seasons.
- Install retaining walls or other stabilizing measures on your property if necessary.
Survival:
- Evacuate immediately if you notice signs of an impending landslide, such as cracking in the ground.
- Move away from steep slopes and unstable terrain.
- Stay indoors if you cannot evacuate safely.
- Listen to emergency services and avoid unnecessary travel during heavy rains.
Sinkholes
Preparation:
- Identify regions with a history of sinkholes.
- Consult with geologists or experts about your specific location.
- Secure your home's foundation and conduct regular inspections for signs of soil subsidence.
Survival:
- If a sinkhole suddenly appears, prioritize safety and evacuate the affected area.
- Stay clear of the sinkhole's edge, as the surrounding ground may be unstable.
- Notify authorities and follow their instructions.
Tidal Waves
Preparation:
- Stay informed about tidal wave risks in coastal areas.
- Develop a family evacuation plan and practice it regularly.
- Have an emergency kit with essential supplies.
Survival:
- If a tidal wave warning is issued, evacuate to higher ground immediately.
- Listen to emergency broadcasts for updates.
- Stay away from coastal areas until authorities declare them safe.
Tornados
Preparation:
- Build or designate a tornado shelter or safe room.
- Create a family tornado plan with designated meeting places.
- Assemble an emergency kit with a battery-operated weather radio.
- Stay informed about tornado watches and warnings.
Survival:
- Seek shelter in the lowest, most central part of your home during a tornado.
- Protect yourself from flying debris and strong winds.
- Listen to weather updates on a battery-operated radio.
- Avoid mobile homes and vehicles during tornado warnings.
Winter Storms
Preparation:
- Stock up on non-perishable food, water, and essential supplies.
- Have warm clothing, blankets, and heating alternatives ready.
- Prepare a vehicle emergency kit if you must travel during winter storms.
- Stay informed about weather forecasts and road conditions.
Survival:
- Stay indoors during severe winter storms and blizzards.
- Conserve heat by closing off unused rooms and using draft stoppers.
- Keep communication devices charged and listen for updates.
- If stranded in your vehicle, stay with it and run the engine intermittently for heat.
Haboobs
Preparation:
- Seal windows and doors to prevent dust infiltration.
- Stock up on non-perishable food and water.
- Create an emergency kit with face masks, goggles, and flashlights.
Survival:
- Stay indoors during haboobs to avoid dust exposure.
- Keep windows and doors closed to minimize dust infiltration.
- Use face masks and goggles if you must go outside.
- Drive cautiously and pull over if visibility is severely reduced.
In the face of natural disasters, preparedness and awareness are your most potent allies. We've covered a diverse range of natural disasters in this guide, each with its specific set of challenges, but the overarching principle remains the same: preparation saves lives. Whether it's securing your home, creating an emergency kit, or having a well-thought-out evacuation plan, taking these steps can significantly improve your chances of surviving and recovering from these destructive events. Moreover, sharing this knowledge with your family, friends, and neighbors can strengthen your community's resilience and support in times of crisis. Remember, being ready for the unexpected is not just a precaution—it's a responsibility we all share in safeguarding ourselves and our communities against the forces of nature.